| WASTE WATER TREATMENT PLANT - (SEWAGE TREATMENT PLANTS) |
|
|
|
SEWAGE TREATMENT PLANTS:
SEWAGE TREATMENT PLANT : MBBR / FAB Technology
 The various toilet streams & waste water are collected in septic tank & led into the raw sewage sump. The sewage is pumped into the Skid mounted Package type Sewage treatment Plant for biological oxidation of organic impurities in presence of activated (biomass) bacterial sludge. The aeration is imparted by Diffused type aerators installed in the tank. The biological treatment method followed is of Moving Bed Bio Reactor (MBBR), also known as Fluidized Bio Reactor ( FAB ). The air is induced in the tank from bottom and it moves upward through moving Media. Moving media due to its movement ensures full utilization of oxygen in the air before it reaches top. The bacteria's which form film on the moving Media utilizes this oxygen and degrades the substrate coming from the sewage water. Increased surface area increases the quantum of the biomass to great extent and thus can sustain shock loads.
MBBR MEDIA: MBBR processes are an excellent solution for common wastewater applications including: • BOD Reduction • Nitrification • Total Nitrogen Removal SEWAGE TREATMENT PLANT : RBC Technology 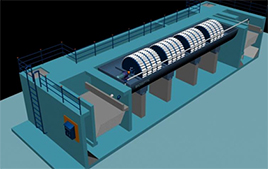 Advantages: • Short contact periods are required because of the large active surface • They are capable of handling a wide range of flows • Sloughed biomass generally has good settling characteristics and can easily be separated from waste stream • Operating costs are low because little skill is required in plant operation • Short retention time • Low power requirements • Elimination of the channelling to which conventional percolators are susceptible • Low sludge production and excellent process control |
||||

 MBBR Technology
MBBR Technology























